Understanding Otitis Media and Azelastine
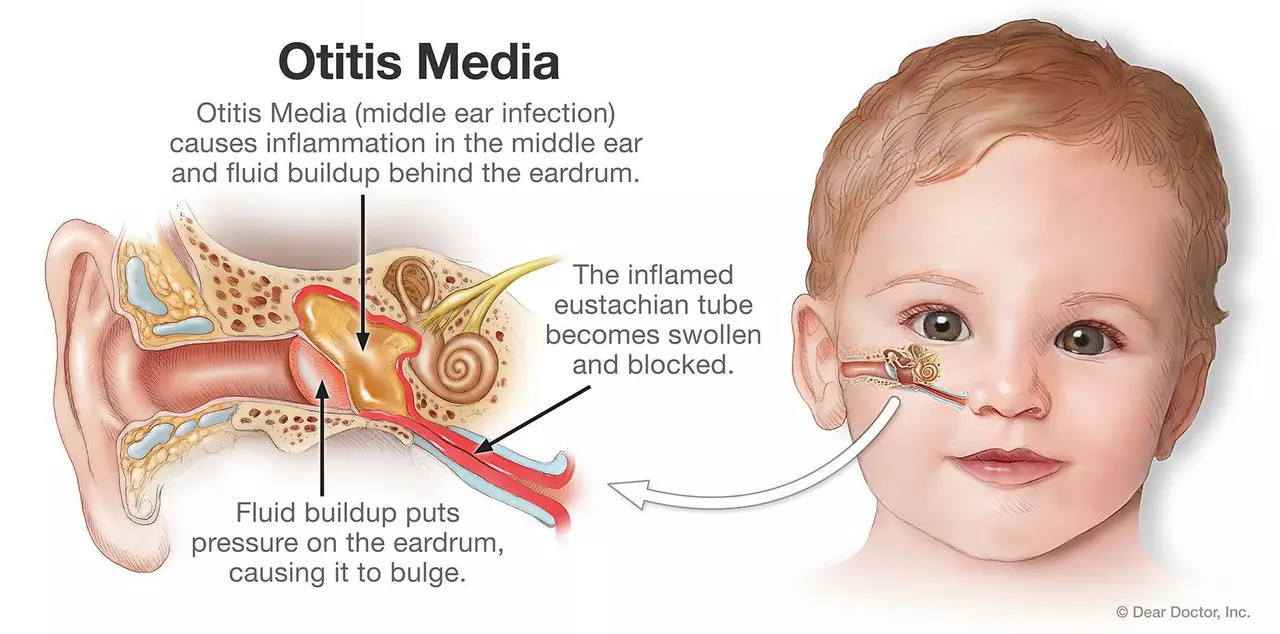
Otitis media, commonly known as a middle ear infection, is a widespread issue that affects many people, especially children. It occurs when there is an inflammation or infection in the middle ear, often caused by bacteria or viruses. On the other hand, azelastine is a medication that has been gaining attention for its potential use in treating otitis media. In this section, we will delve into the basics of otitis media and azelastine, setting the foundation for understanding their connection.
As mentioned earlier, otitis media is an inflammation of the middle ear, which can be acute or chronic. Acute otitis media is characterized by sudden onset, and it usually resolves within a few weeks. Chronic otitis media, however, is a long-lasting condition that can persist for months, or even years. Both forms of otitis media can lead to complications such as hearing loss, ear pain, and fever.
Azelastine, on the other hand, is an antihistamine and mast cell stabilizer, which has been primarily used to treat allergic rhinitis. It works by blocking the action of histamine, a substance released by the immune system during an allergic reaction, thereby reducing inflammation and swelling.
Exploring the Connection Between Azelastine and Otitis Media
Recent studies have been looking into the potential benefits of using azelastine to treat otitis media. The connection between the two lies in the fact that both conditions involve inflammation and swelling. Since azelastine is known for its effectiveness in reducing inflammation in cases of allergic rhinitis, researchers are now investigating if it can have similar positive effects on otitis media.
With its anti-inflammatory properties, azelastine has the potential to alleviate the symptoms and complications of otitis media. Moreover, by reducing the swelling in the middle ear, it may also help with drainage, which is crucial for the healing process.
However, it is essential to note that the connection between azelastine and otitis media is still being explored. More research is needed to determine the effectiveness and safety of azelastine as a treatment option for otitis media.
The Role of Azelastine in Preventing Otitis Media
Another area of interest is the potential role of azelastine in preventing otitis media. Since allergies can sometimes lead to or exacerbate ear infections, it is believed that by controlling allergic symptoms, azelastine could help prevent the onset or recurrence of otitis media.
By stabilizing mast cells and blocking histamine, azelastine can effectively reduce inflammation and swelling in the nasal passages. This, in turn, can help improve eustachian tube function, which is responsible for draining fluid from the middle ear. A well-functioning eustachian tube is crucial in preventing the buildup of fluid in the middle ear, which can lead to infection.
While this connection is promising, more research is required to establish the preventive role of azelastine in otitis media.
Azelastine as a Potential Alternative to Antibiotics
Antibiotics are often prescribed to treat bacterial otitis media. However, the increasing emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria has led researchers to look for alternative treatment options. Azelastine, with its potential anti-inflammatory effects on the middle ear, is being considered as one such alternative.
Although azelastine cannot directly kill bacteria like antibiotics, its ability to reduce inflammation and swelling in the middle ear could help improve drainage and create an environment that is less conducive to bacterial growth.
That being said, more extensive clinical trials are needed to determine if azelastine can be an effective alternative to antibiotics in treating otitis media.
Practical Considerations and Future Research
While the connection between azelastine and otitis media is promising, it is important to remember that more research is needed to establish its effectiveness and safety. As a patient or parent of a child with otitis media, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before considering azelastine as a treatment option.
Future studies should focus on comparing the efficacy of azelastine with other treatment options, such as antibiotics, in managing otitis media. Additionally, research should also investigate the optimal dosing and duration of azelastine treatment for otitis media, as well as any potential adverse effects.
In conclusion, the connection between azelastine and otitis media is an intriguing area of research that holds promise for improving the management of this common ear infection. However, it is vital to approach this connection with cautious optimism and to wait for more definitive evidence before incorporating azelastine into otitis media treatment plans.

Warren Nelson
Azelastine might actually help with ear fluid drainage, worth a look.
Jennifer Romand
The academic discourse on otitis media often drifts into the realms of cliché, yet this piece attempts to stitch together histamine antagonism and middle‑ear pathology with a flair that borders on theatrical.
Kelly kordeiro
The potential role of azeluric agents such as azelastine in otologic pathology warrants rigorous scholarly scrutiny.
Contemporary otolaryngological literature delineates a complex interplay between mucosal inflammation and eustachian tube dysfunction.
Azelastine, as a potent histamine H1-receptor antagonist, exhibits mast cell stabilising properties that may attenuate mucosal edema.
By mitigating such edema, the hypothesised enhancement of middle‑ear aeration could conceivably reduce the incidence of serous effusion.
Empirical investigations, albeit preliminary, have reported modest reductions in tympanic membrane bulging subsequent to intranasal azelastine administration.
Nevertheless, the paucity of double‑blind, placebo‑controlled trials renders any extrapolation to clinical practice speculative at best.
Moreover, the pharmacokinetic profile of azelastine, characterised by limited systemic absorption, may curtail adverse systemic sequelae.
This pharmacodynamic attribute aligns with contemporary imperatives to curtail antibiotic overuse and attendant resistance.
In the context of paediatric otitis media, where bacterial colonisation often follows viral prodromes, anti‑inflammatory adjuncts assume heightened relevance.
The immunological milieu within the nasopharynx, replete with cytokine cascades, is amenable to modulation by antihistaminic therapy.
Yet, the etiological heterogeneity of otitis media, encompassing bacterial, viral, and allergic components, necessitates a stratified therapeutic algorithm.
Consequently, azelastine may find its optimal utility not as a monotherapy but as part of a multimodal regimen.
Future research directives should encompass dose‑response analyses, optimal delivery mechanisms, and longitudinal safety assessments.
Such investigations would substantiate whether azelastine can viably supplant or supplement conventional antibiotic protocols.
Until such evidentiary foundations are erected, clinicians are advised to exercise circumspection when contemplating off‑label azelastine usage.
Chris Fulmer
I appreciate the balanced overview; the link between nasal inflammation and eustachian tube function is often under‑discussed, and azelastine’s mast‑cell stabilising effect could be a gentle bridge between allergy control and ear health.
William Pitt
Exactly, Chris. If you’re already treating allergic rhinitis with azelastine, you might get the added bonus of fewer ear infections without adding another drug to the mix.
Jeff Hershberger
Seems like a colorful idea, but we need hard data before folks start swapping pills for sprays.
Jesse Najarro
True, Jeff. The concept is intriguing, yet the science is still in its infancy.
Dan Dawson
Not bad, could be worth a shot.
Lawrence Jones II
From a pharmacodynamic perspective, azelastine’s H1 antagonism could theoretically reduce nasopharyngeal mucosal hyperemia, thereby improving ET patency 🤓. Still, we await Phase‑III data.
Robert Frith
Honestly this sounds like some wankers trying to sell a new miracle spray, lol. If it works, great, if not, wasted cash.
Albert Gesierich
Just a heads‑up: "azelastine" is spelled with an "e" after the "l", not "azalastine". Accuracy matters when citing meds.
Brad Tollefson
Good point, Albert. The article does use the correct spelling throughout, which is reassuring for readers.
Paul van de Runstraat
Oh, sure, because a nasal spray will magically fix ear infections. Next you'll tell us chocolate cures diabetes.
Suraj Midya
We must be careful not to undermine the proven efficacy of antibiotics. Over‑optimism about alternatives can lead to dangerous neglect.
ashish ghone
Hey everyone, I just wanted to say that while the science is still emerging, I’ve personally seen kids on azelastine for allergies have fewer ear infections-so I’m cautiously hopeful. It’s always good to have another tool in the toolbox, especially when dealing with resistant bacteria. 🌟 Keep an eye out for upcoming trials!
steph carr
Positive vibes! If future studies back this up, azelastine could be a win‑win for allergy sufferers and those prone to ear infections.
Vera Barnwell
Let’s not forget that pharma loves to push “alternative” uses for their products to boost sales. While azelastine looks promising, we should demand transparent, independent research before embracing it widely.
David Ross
Indeed, the potential is intriguing, and the safety profile appears favorable; however, rigorous clinical trials are essential, and we must await solid evidence before altering standard practice.
Henry Seaton
Sounds like a decent idea, but keep it simple-don’t replace antibiotics unless proven.
Baby Thingie
Data pending; use judiciously.