Estrogen: What It Does and When to Act
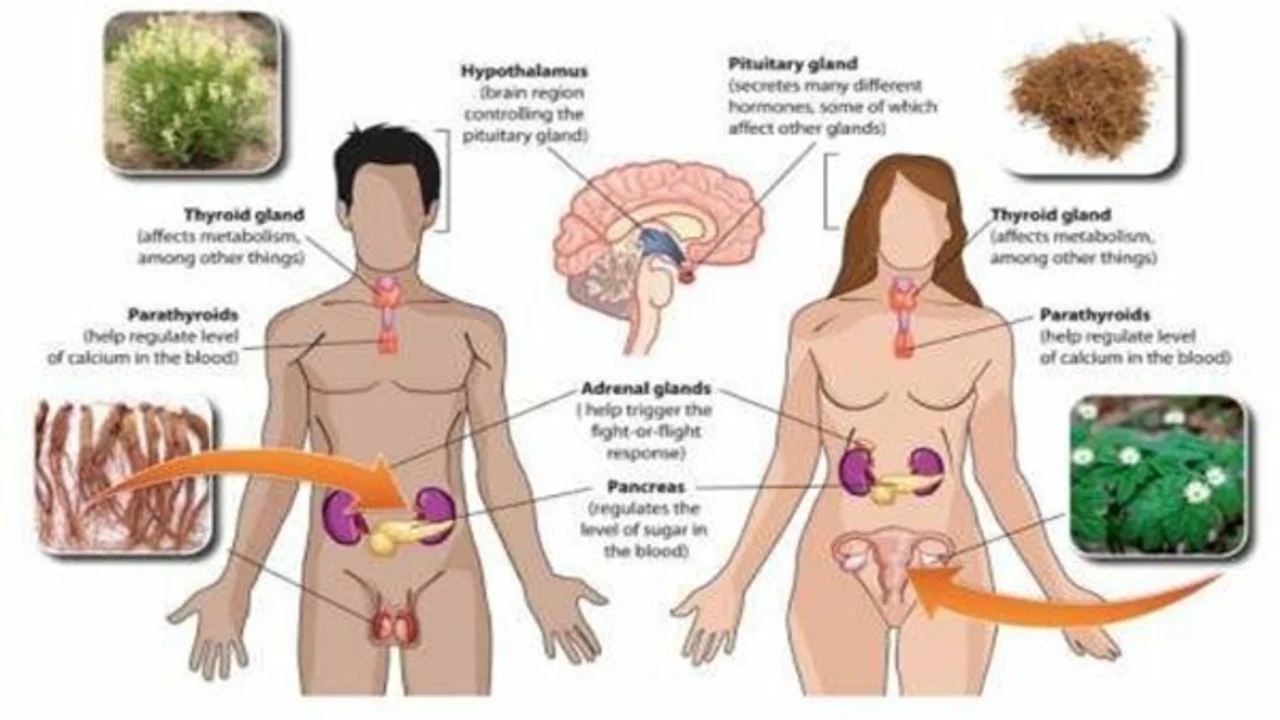
Feeling tired, losing your sex drive, and waking up with hot flashes? Those are common signs many people link to low estrogen. Estrogen isn’t just about periods — it affects bones, mood, skin, and heart health. This page helps you spot real symptoms, understand basic treatment options, and take safer steps toward balance.
Common signs and when to test
Low estrogen often shows up as irregular periods, night sweats, vaginal dryness, mood swings, and trouble sleeping. Women approaching menopause or who’ve had surgery to remove ovaries are more likely to notice it. High estrogen can cause bloating, breast tenderness, heavy periods, and sometimes headaches. If symptoms affect daily life, ask your clinician for a simple blood test (usually estradiol) and a clear plan.
Don’t self-diagnose based on a single symptom. Fatigue or mood changes can come from many causes. A targeted blood test plus a short medical history gives real answers fast.
Treatment options and what to expect
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is the most direct way to raise estrogen. Options include pills, transdermal patches, gels, and vaginal creams or rings. Patches and gels often have steadier hormone levels and lower clot risk than some pills. For vaginal dryness only, local low-dose estrogen creams or rings work well and have minimal systemic effects.
Non-hormone treatments can help too: certain antidepressants ease hot flashes, and lubricants or moisturizers relieve vaginal dryness. Lifestyle changes—regular weight-bearing exercise, a balanced diet with calcium and vitamin D, and quitting smoking—support bones and lower some risks linked to low estrogen.
All treatments carry trade-offs. Estrogen can raise the risk of blood clots and, depending on dose and duration, may affect breast cancer risk. Your age, medical history, and personal risk factors matter more than headlines. A short trial with follow-up lets you see benefits vs side effects quickly.
Medications you already take can change estrogen levels. For example, some seizure drugs affect hormones, and certain herbal supplements interact with prescription meds. Always tell your provider about every medication and supplement you use.
Quick practical tips: track symptoms in a simple diary, bring medication lists to appointments, and ask for the lowest effective dose if you start HRT. If you’re worried about long-term risks, ask about non-hormone alternatives and routine screening plans.
Want deeper reads on related topics like sexual function, hair loss, or drug interactions? Our site has clear articles on impotence, finasteride alternatives, and medication safety. If something feels off, get testing and a plain plan — most hormone issues are manageable once you know what’s going on.
Premarin: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects, and More
Premarin is a well-known medication used mainly for hormone replacement therapy, especially by women going through menopause. This article explains what Premarin is, how it works, who might benefit from it, known side effects, and tips for safe use. Learn about its history, controversies, common questions, and alternatives in an honest and easy-to-understand style. Whether you're considering Premarin or just curious about hormones, this guide has you covered. Get helpful advice so you can make decisions with confidence.
MoreEstrogen and your skin: the importance of maintaining hormonal balance
In my exploration of the connection between estrogen and skin, I've realised that maintaining hormonal balance is crucial for skin health. Estrogen, a vital hormone in women, plays a significant role in keeping our skin youthful and healthy. An imbalance can lead to issues like acne, dryness, and premature aging. It's important for us to understand our bodies and make lifestyle choices that support hormonal balance. This knowledge puts us in a better position to manage our overall health, including the health of our skin.
More